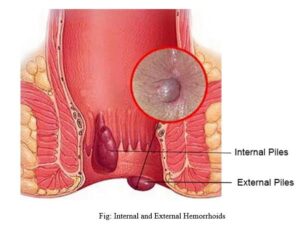
Managing piles and leading a normal life: 9 Expert Tips
Managing piles (hemorrhoids) effectively can help you live a normal, active life without the discomfort or disruption they can cause. Here are 9 expert tips to manage piles: 1. Maintain a High-Fiber Diet A high-fiber diet helps to soften stools, making bowel movements smoother and reducing the strain on hemorrhoids. Include foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in your daily meals. Tip: Gradually increase fiber intake to prevent bloating and gas. 2. Stay Hydrated Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Proper hydration softens stools and prevents constipation, which can exacerbate hemorrhoids. Tip: Aim for at least 8 cups (2 liters) of water a day, more if you’re active. 3. Use Stool Softeners or Laxatives (if necessary) If you suffer from chronic constipation, a stool softener or a mild laxative can help reduce the strain during bowel movements. Tip: Consult with your doctor before using any over-the-counter products regularly. 4. Avoid Prolonged Sitting Sitting for extended periods can put pressure on the anal area, worsening piles. Get up and walk around every 30-45 minutes if you have a desk job or long commute. Tip: Consider using a standing desk to help relieve pressure on your bottom. 5. Practice Proper Bathroom Habits Don’t strain during bowel movements. Avoid sitting on the toilet for too long. If you’re having difficulty passing stools, try gentle, non-straining techniques or use a footstool to elevate your legs. Tip: Always wipe gently after bowel movements to avoid irritation. 6. Warm Sitz Baths Soaking the affected area in warm water for 10-15 minutes can help soothe pain, itching, and inflammation associated with hemorrhoids. Tip: Add a small amount of Epsom salt to the bath for added relief, but avoid harsh soaps or scented products that could irritate. 7. Use Topical Treatments Over-the-counter creams, ointments, or suppositories containing hydrocortisone or witch hazel can help reduce itching, inflammation, and pain. Tip: Apply the cream only as directed to avoid thinning the skin or causing more irritation. 8. Exercise Regularly Regular exercise helps to maintain a healthy weight, prevent constipation, and improve blood circulation, reducing the pressure on hemorrhoids. Tip: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise, such as walking or swimming, most days of the week. 9. Seek Medical Treatment When Necessary If your hemorrhoids become very painful, bleeding occurs, or you experience significant discomfort despite home care, consult a healthcare professional. They may recommend treatments like rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, or even surgery in severe cases. Tip: Don’t ignore persistent symptoms—early intervention can prevent complications. By following these expert tips, many people with hemorrhoids can lead a normal, active life. However, always consult with a healthcare professional to tailor a treatment plan suited to your individual needs.

Everything You Need to Know About Gallstones
Gallstones are solid particles that form in the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver. The gallbladder stores bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver that helps break down fats. Gallstones can vary in size, ranging from tiny grains to large stones, and can sometimes lead to complications if they obstruct the bile ducts. Here’s everything you need to know about gallstones: 1. Types of Gallstones Cholesterol Gallstones: These are the most common type, made mostly of hardened cholesterol. They form when there is too much cholesterol in the bile. Pigment Gallstones: These are smaller and darker, made from excess bilirubin (a substance produced when the liver breaks down red blood cells). They are more common in individuals with liver diseases or certain blood disorders. 2. Causes of Gallstones Imbalance in Bile Composition: If the bile contains too much cholesterol, too much bilirubin, or not enough bile salts, it can lead to gallstone formation. Obesity: Obesity increases cholesterol production and decreases gallbladder function, which can lead to gallstone formation. Dietary Factors: A high-fat, high-cholesterol diet can increase the risk of gallstones. Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can increase cholesterol levels in bile and reduce gallbladder emptying. Age and Gender: Women, especially those over 40, are at a higher risk. Men can also develop gallstones, but at a lower rate. Genetic Factors: Family history plays a role in susceptibility to gallstones. 3. Symptoms Gallstones may not always cause symptoms, which is referred to as “silent” gallstones. However, when symptoms do occur, they include: Pain: Typically in the upper right abdomen or in the center of the abdomen. The pain may be sudden and intense, known as a gallbladder attack or biliary colic. Nausea and Vomiting: Often accompanying the pain. Indigestion: Especially after eating fatty foods. Jaundice: If a gallstone blocks a bile duct, it may cause a buildup of bilirubin, leading to yellowing of the skin and eyes. Fever and Chills: These symptoms can occur if a gallstone causes an infection in the gallbladder or bile ducts. 4. Diagnosis Ultrasound: The most common and effective way to detect gallstones. CT Scan or MRI: Sometimes used to identify complications or provide a clearer image. HIDA Scan: This test tracks the flow of bile from the liver to the small intestine and can identify issues with gallbladder function. 5. Treatment Options Observation: If gallstones are not causing symptoms, treatment may not be necessary, and the condition is monitored. Medications: Some medications can help dissolve cholesterol gallstones, but this is a slow process and not always effective. Cholecystectomy: The most common treatment for symptomatic gallstones is surgical removal of the gallbladder, a procedure known as cholecystectomy. This can be done using a minimally invasive technique called laparoscopic surgery. Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): This procedure is used if gallstones are blocking a bile duct. It involves using an endoscope to remove or break up the stones. 6. Lifestyle Changes Diet: Eating a low-fat, high-fiber diet can help prevent gallstones. Avoiding excessive amounts of cholesterol-rich foods is recommended. Regular Exercise: Maintaining a healthy weight and staying active can reduce the risk of gallstones. Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids, especially water, can help maintain healthy bile flow. 7. Complications Cholecystitis: Inflammation or infection of the gallbladder, often caused by a blocked bile duct. Pancreatitis: Gallstones can block the pancreatic duct, leading to inflammation of the pancreas. Cholangitis: Infection of the bile ducts, often associated with a bile duct obstruction caused by a gallstone. Gallbladder Cancer: Though rare, long-term inflammation from gallstones can increase the risk of gallbladder cancer. 8. Prevention Maintain a healthy weight: Rapid weight loss, such as from fad diets or weight loss surgery, can increase the risk of gallstones. Avoid long periods without eating: Skipping meals or fasting can cause the gallbladder to become sluggish. Increase fiber intake: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help prevent gallstone formation. 9. After Gallbladder Removal (Cholecystectomy) Digestive Changes: Without a gallbladder, bile flows directly from the liver into the small intestine, which can sometimes lead to digestive issues like diarrhea, particularly after eating fatty meals. Long-Term Outlook: Most people recover fully from gallbladder removal and can live a normal life without it. In conclusion, gallstones are common and can range from harmless to causing severe complications. Early detection and appropriate treatment, such as lifestyle changes or surgery, can help manage symptoms and prevent serious problems. If you suspect you have gallstones, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for diagnosis and guidance.
Robotic Surgery in North-East India: 7 Incredible Reasons It’s Revolutionizing Healthcare
Robotic Surgery in North-East India: 7 Incredible Reasons It’s Revolutionizing Healthcare Robotic Surgery is a type of minimally invasive surgery where doctors use a robotic system to perform operations with more precision, flexibility, and control than traditional techniques.Surgeons control robotic arms through a computer console.The system provides a magnified, detailed view of the surgical area. Robotic surgery in North-East India is rapidly transforming the healthcare landscape, providing cutting-edge technology that brings world-class medical care to the region. This innovative approach to surgery offers unparalleled precision, faster recovery times, and reduced risks, making it a game-changer for both patients and healthcare providers. 1. What is Robotic Surgery? Robotic surgery in North-East India involves the use of advanced robotic systems to perform complex surgical procedures with exceptional accuracy. This technology allows surgeons to operate through tiny incisions, minimizing trauma to the body and significantly speeding up the recovery process. 2. Precision and Accuracy One of the most significant advantages of robotic surgery in North-East India is its precision. The robotic system’s advanced technology allows for highly accurate surgical procedures, reducing the risk of complications and ensuring better outcomes for patients. This level of precision is especially crucial in delicate surgeries involving vital organs or nerves. 3. Minimally Invasive Surgery Robotic surgery is minimally invasive, meaning it requires smaller incisions than traditional surgery. For patients in North-East India, this results in less pain, minimal scarring, and quicker recovery times. The minimally invasive nature of robotic surgery also reduces the overall stress on the body, allowing patients to return to their daily activities sooner. 4. Faster Recovery Times Patients undergoing robotic surgery in North-East India benefit from faster recovery times due to the less invasive nature of the procedures. With smaller incisions and reduced trauma to the body, patients can expect shorter hospital stays and a quicker return to normal life. 5. Lower Risk of Infection Smaller incisions mean a lower risk of post-surgical infections, a critical advantage for patients in North-East India. This reduced risk of infection is particularly important in regions where access to continuous post-operative care may be limited. 6. Local Access to Advanced Healthcare The introduction of robotic surgery in North-East India is especially significant given the region’s unique healthcare challenges. In the past, patients often had to travel long distances to access advanced medical treatments. With robotic surgery now available locally, patients can receive world-class care closer to home, reducing travel expenses and the associated stress. 7. Empowering Local Healthcare Providers The adoption of robotic surgery in North-East India is not just beneficial for patients but also empowers local healthcare providers. The presence of this advanced technology in the region helps train and enhance the skills of local surgeons and medical staff, fostering a more capable and confident healthcare workforce. Success Stories in North-East India Several hospitals in North-East India have already implemented robotic surgery with remarkable success. These institutions have performed complex surgeries, such as urological, gynecological, and cardiac procedures, with excellent outcomes. Patients have reported less post-operative pain, quicker recoveries, and overall improved quality of life. To learn more about the benefits of robotic surgery, you can refer to Mayo Clinic’s resource on robotic surgery and Cleveland Clinic’s insights on robotic surgery. Conclusion Robotic surgery in North-East India is more than just a technological advancement; it is a transformative force that is reshaping healthcare in the region. As more hospitals adopt this cutting-edge technology, the people of North-East India can look forward to better access to world-class medical care without leaving their region. The future of healthcare in North-East India is bright, thanks to the power of robotic surgery.
